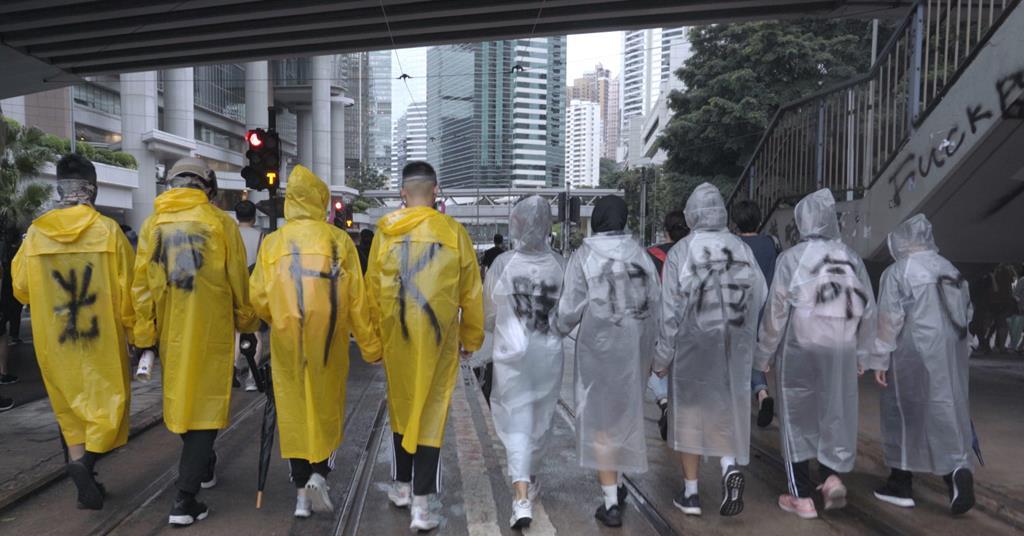
In June, the Government introduced amendments to the Film Censorship Guidelines for Censors to provide censors with clearer guidance to consider the implications of a film on national security, so as to decide whether the film is suitable for exhibition and its classification.
The proposed amendments [to Cap. 392 Film Censorship Ordinance] announced today are ‘designed’ to quote “enhance the film censorship regulatory framework, with a view to ensuring more effective fulfilment of the duty to safeguard national security as required by the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Safeguarding National Security in the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, as well as preventing and suppressing acts or activities that may endanger national security.”
Unveiling the new bill, Secretary for Commerce and Economic Development Edward Yau Tang-wah said there would be NO appeal mechanism for bans issued on security grounds.
Yau continued “Amendments giving the Chief Secretary power to revoke the certificates of approval previously issued for films, there is a chance that past movies could be banned from public screening,”
In response to the question: How do you define a movie as ‘contrary to interests of national security? Yau answered ” NSL is the main reference New ordinance also goes into more details covering what might endorse/support/promote/glorify/encourage/incite such act/activity which might endanger national security”
The key proposals in the new Bill are:
(a) to set out explicitly that a censor should consider whether the exhibition of a film would be contrary to the interests of national security, so as to provide clear statutory backing for a censor to give due consideration to national security when making film decisions;
(b) to empower the Chief Secretary for Administration to direct the Film Censorship Authority to revoke certificates of approval or certificates of exemption previously issued for films if their exhibition would be contrary to the interests of national security;
(c) the Secretary for Commerce and Economic Development (SCED) may grant extension of time for a period of no more than 28 days each time for a censor to make a decision where the Authority is of the opinion that the exhibition of the film might be contrary to the interests of national security, allowing sufficient time for the censor to deal with cases that may involve national security considerations and to seek legal advice; and
(d) to disapply [remove] the relevant sections that empower the Board of Review (Film Censorship) to consider requests for review of the decisions of the Authority or a censor, for decisions made on national security grounds.
With no appeal now allowed against the censors decision, has the government killed off both Hong Kong’s film industry and it’s cinemas?
Other amendments to the current law the government wants to make include:
(a) to specify that a censor can request the addition of a specific notice to a film, to serve as a reminder to viewers (or their parents) to mitigate potentially undesirable effects;
(b) to empower the Authority [OFNAA] to require the holders of certificates of exemption or certificates of approval to provide information about the exhibition of their respective films, such as the date, time and venue, and to empower an inspector authorised by the Authority to enter and search any place with the authority of a judicial warrant in order to enhance the inspector’s ability to take enforcement action;
(c) to impose heavier penalties for exhibiting films that are not exempted or approved, raising the maximum penalty to imprisonment for three years and/or a fine of $1 million;
(d) to remove the specified number of non-official members to be appointed, as well as to empower the SCED [Secretary for Commerce and Economic Development] to appoint a public officer as his representative to attend and vote at the Review Board meetings, in order to allow greater flexibility to determine the composition of the Review Board.

Illustration: Derek Zheng





